Cell Ranger6.1, printed on 04/23/2025
Adaptive immunity is based on clonal selection and expansion from a repertoire of T and B lymphocytes bearing a diversity of cell-surface receptors and antibodies that recognize specific antigens. The enormous diversity of lymphocyte receptors and antibodies expressed from a relatively small number of gene segments is largely made possible through V(D)J recombination. The hypervariable recombined V(D)J transcripts in turn determine the affinity of the Complementary Determining Regions (CDRs) to bind to specific epitopes. See the Glossary for more details.
The 10x Genomics Chromium Next GEM Single Cell Immune Profiling Solution enables simultaneous analysis of these libraries at single cell resolution for the same set of cells:
This makes the Immune Profiling Solution ideal for understanding the key features of an adaptive immune response and their impact on other genomic analytes, disease severity, therapy, and outcome.
Analysis of these data types can be performed using the latest versions of Cell Ranger. The following illustration depicts how the cellranger multi pipeline can be used to analyze FASTQ data derived from these three Immune Profiling library types from the same GEM Well:
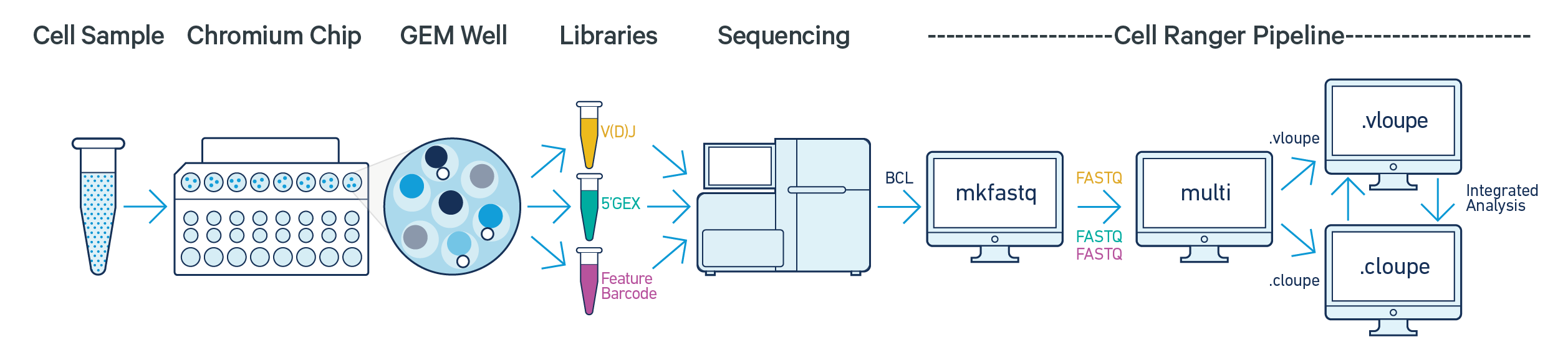
Cell Ranger includes five pipelines relevant to Immune Profiling data analysis:
cellranger mkfastq demultiplexes raw base call (BCL) files generated by Illumina sequencers into FASTQ files. It is a wrapper around Illumina's bcl2fastq, with additional useful features that are specific to 10x libraries and a simplified sample sheet format.
cellranger vdj takes FASTQ files from cellranger mkfastq or bcl2fastq for V(D)J libraries and performs sequence assembly and paired clonotype calling. It uses the Chromium cellular barcodes and UMIs to assemble V(D)J transcripts per cell. Clonotypes and CDR3 sequences are output as a .vloupe file which can be loaded into Loupe V(D)J Browser.
cellranger count takes FASTQ files from cellranger mkfastq or bcl2fastq for 5' Gene Expression and/or Feature Barcode (cell surface protein or antigen) libraries and performs alignment, filtering, barcode counting, and UMI counting. It uses the Chromium cellular barcodes to generate feature-barcode matrices, determine clusters, and perform gene expression analysis. The cellranger count pipeline outputs a .cloupe file which can be loaded into Loupe Browser for interactive visualization, clustering, and differential expression analysis.
cellranger multi takes FASTQ files from cellranger mkfastq or bcl2fastq for any combination of 5' Gene Expression, Feature Barcode (cell surface protein or antigen) and V(D)J libraries from a single gem-well. It performs alignment, filtering, barcode counting, and UMI counting on the Gene Expression and/or Feature Barcode libraries. It also performs sequence assembly and paired clonotype calling on the V(D)J libraries. Additionally, the cell calls provided by the gene expression data are used to improve the cell calls inferred by the V(D)J library.
cellranger aggr aggregates outputs from multiple runs of cellranger count/vdj/multi. The aggr pipeline normalizes the individual gene expression and feature barcode runs to the same sequencing depth, recomputes the feature-barcode matrices and performs analysis on the combined data. The pipeline also recomputes the V(D)J clonotype grouping on the combined data.
The .cloupe files and the .vloupe files output by the pipelines can be overlaid for an integrated analysis with Loupe Browser and Loupe V(D)J Browser. Refer to Analysis of Multiple Library Types for more information.