Cell Ranger6.0, printed on 04/02/2025
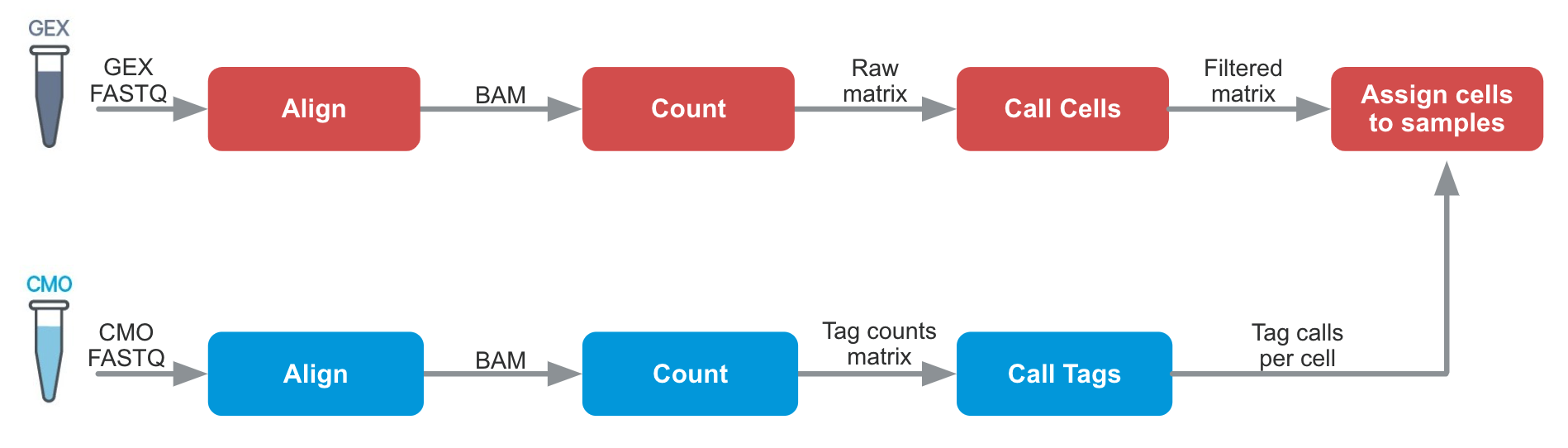
Cell Ranger 6.0 introduces support for Cell Multiplexing with the cellranger multi pipeline. The algorithms are similar to cellranger count in many ways, but an additional tag calling step is required:
Cell-associated barcodes are identified as singlets, multiplets, or blanks (considered to have lower than expected tag counts for all tags used) according to a probabilistic model. A key benefit of this algorithm is the ability to detect and filter most multiplets and blanks from the data.
Cell Ranger 6.0 features a probabilistic model for assigning Cell Multiplexing Oligo (CMO) tags to cell-associated barcodes. The algorithm employs a latent variable model over a state space composed of each sample used in the experiment. To make the algorithm computationally tractable, the model explicitly accounts for the type and quantity of the different multiplets expected. For example, there is a “Blanks” state for barcodes associated with cells that have not been stained with any tag, a singlet state for each tag used in the experiment, and different states for each type of multiplet based on how many tags were used (up to 12 supported).
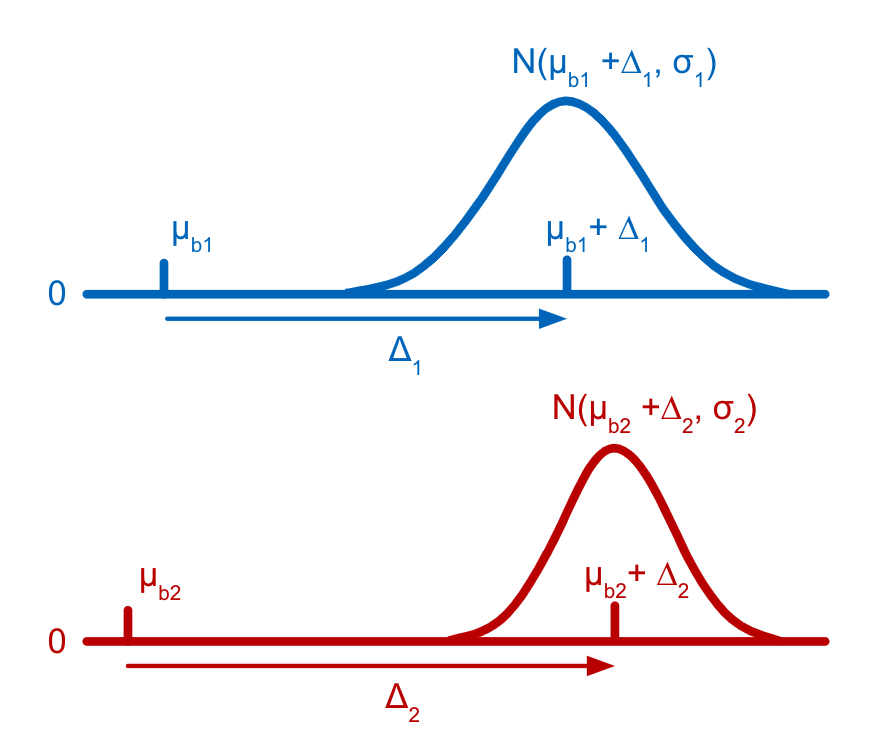
Each tag is assumed to have a distribution of counts amongst cells that have not been stained with the tag (background distribution) and another distribution of counts amongst cells that have been stained with the tag (signal distribution). Both the background and the signal distribution are assumed to be Gaussian with different means but the same variance. The parameters for the distributions of counts for latent states are efficiently derived as linear combinations of the individual cell-states (stained or not) present in the latent state, allowing states which are rarely, or never, observed in the data to still be accurately estimated. The parameters for the Gaussian distributions and the latent state assignments for each barcode are estimated using a customization of the Expectation-Maximization (EM) algorithm (Dempster et al., 1977).
Cell Ranger models the count distribution of each CMO tag with the following assumptions:
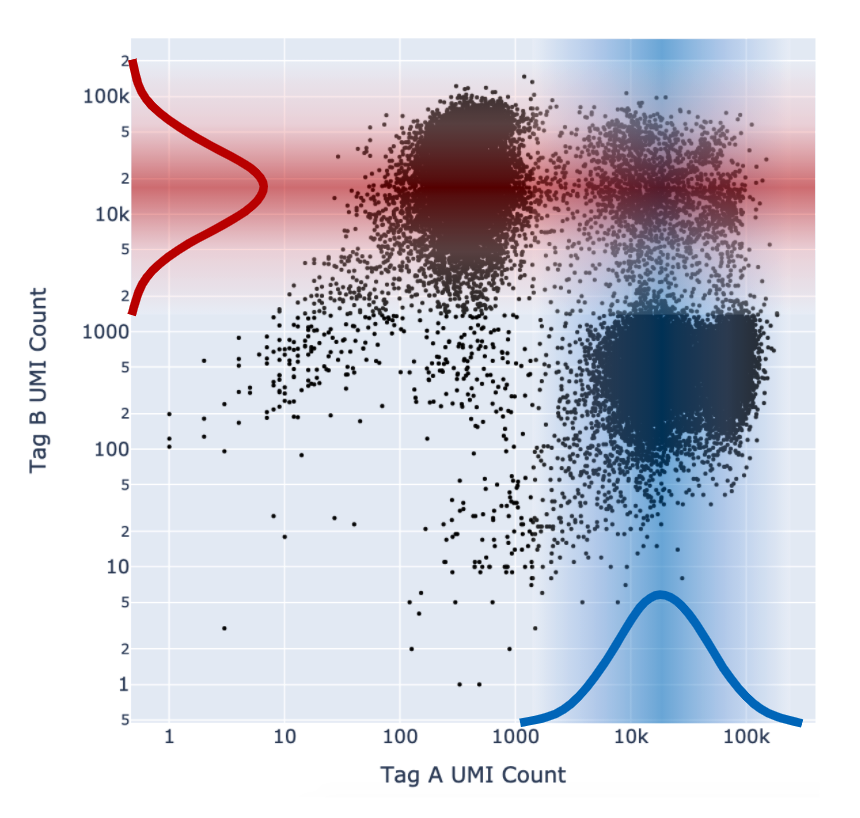
When the EM optimization converges, Cell Ranger calculates, for each barcode, the probability that it belongs to each latent state in the model. Following this, Cell Ranger combines all the different multiplet states into one coarse-grained Multiplet state by summing their probabilities.
For each barcode:
Cell Ranger adds a fifth "Unassigned" category for cells that cannot be confidently assigned to any other state. This is done by enforcing a minimum confidence threshold to filter out low confidence assignments, as detailed below in the “Confidence thresholding” section. Being more stringent about the minimum confidence necessary to make an assignment results in greater accuracy (lower mis-assignment rate) at the cost of yield (fewer singlets).
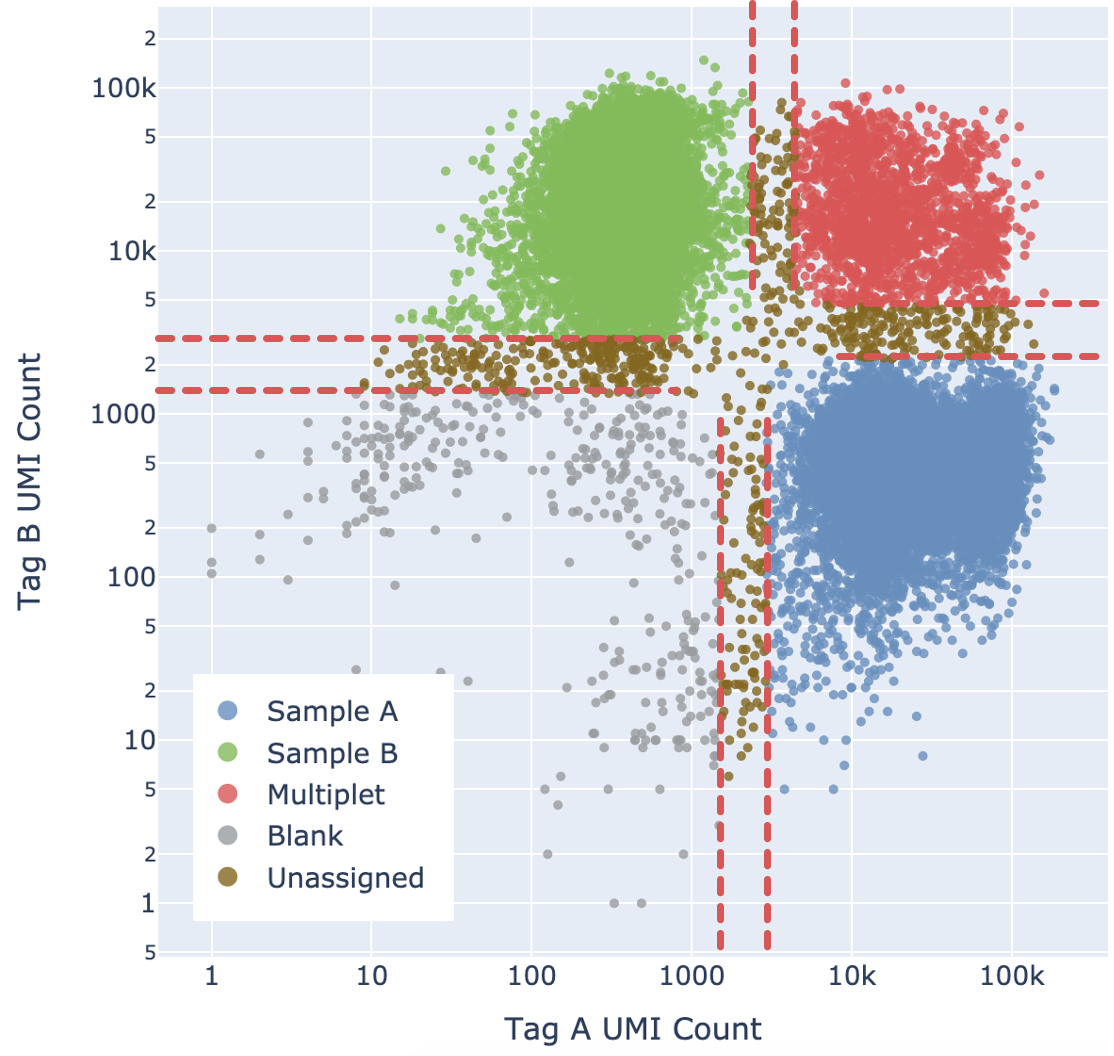
Ultimately barcodes that are classified as Multiplet, Blanks, or Unassigned are filtered out. Note that the algorithm cannot filter out homo-multiplets, i.e. multiplets containing only one tag.
There is an inherent trade-off between yield (number of singlets assigned a single tag) and accuracy (as defined by the rate of mis-assignment). Being more stringent about the minimum confidence necessary to make an assignment results in greater accuracy (lower mis-assignment rate) at the cost of yield (fewer singlets).
Based on analysis of the yield-accuracy tradeoff in representative datasets, a default minimum confidence threshold for assignments was set at 0.9. (Since these probabilities are not exact, this corresponds typically to a mis-assignment rate significantly less than 1%.) When the most likely state for a barcode has a likelihood of less than 0.9, we label it as "Unassigned". Only barcodes with a singlet likelihood of 90% or greater are considered singlets by the model and assigned to a sample.
For particular datasets of interest, the user may wish to tolerate a higher rate of mis-assignment in order to obtain more singlets to include in their analysis, or a lower rate of mis-assignment at the cost of obtaining fewer singlets. As of Cell Ranger 6.0.2, users can adjust the default threshold by changing the min-assignment-confidence parameter in the multi config CSV file.