Cell Ranger7.1, printed on 03/11/2025
| New in Cell Ranger v7.0: Intronic reads are counted by default for whole transcriptome gene expression data. For more information, see our recommendation on including introns for gene expression analysis page |
| After June 30, 2023, new Cell Ranger releases will no longer support Targeted Gene Expression analysis. |
The 5' Chromium Next GEM Single Cell Immune Profiling Solution with Feature Barcode technology enables simultaneous profiling of the V(D)J repertoire, cell surface protein, antigen, and gene expression (GEX) data. The cellranger multi pipeline analyzes these multiple library types together, enabling more consistent cell calling between the V(D)J and gene expression data.
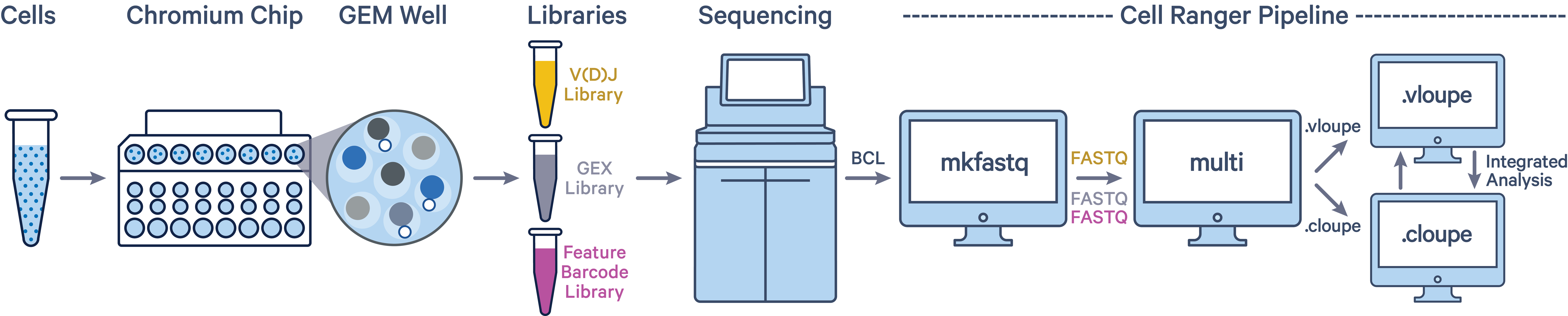
The cellranger multi pipeline takes a config CSV with paths to FASTQ files from cellranger mkfastq, bcl2fastq, or BCL Convert for any combination of 5' Gene Expression, Feature Barcode (cell surface protein, antibody/antigen, or CRISPR), and V(D)J libraries from a single GEM well. It performs alignment, filtering, barcode counting, and UMI counting on the Gene Expression and/or Feature Barcode libraries. It also performs sequence assembly and paired clonotype calling on the V(D)J libraries. Additionally, the cell calls provided by the gene expression data are used to improve the cell calls from the V(D)J data. Visit the multi tutorial page for self-guided and video tutorials on running cellranger multi.
| The 5' Chromium Next GEM Immune Profiling Solution does not support cell multiplexing, and Cell Ranger does not support demultiplexing 5' libraries. |
Pipeline recommendation depends on the combination of input libraries. In general, cellranger multi is the recommended pipeline for analyzing a combination of Gene Expression and V(D)J libraries (with or without Feature Barcode libraries) sequenced from the same sample.
This table summarizes a few popular library combinations and their corresponding pipeline recommendations:
| Library combination | multi | Other pipelines |
|---|---|---|
| GEX | Supported | count |
| VDJ | Supported | vdj |
| Antibody | Supported | count |
| CRISPR | Supported | count |
| Antigen (BEAM) | Not allowed | None |
| GEX + VDJ | Recommended | count and vdj |
| GEX + VDJ + Antibody | Recommended | count and vdj |
| GEX + VDJ + Antibody + CRISPR | Recommened | count and vdj |
| GEX + VDJ + Antibody + Antigen (BEAM) | Required | None |
| GEX + Antigen | Not allowed | None |
The cellranger multi pipeline improves cell calls in the V(D)J dataset by discarding any cells that were not also called in the corresponding 5' Gene Expression dataset. By assigning cells that are called in the V(D)J results but not in the 5' Gene Expression results as background GEMs in the V(D)J data, cellranger multi mitigates any overcalling issues that may arise in V(D)J data. This improved cell calling is only possible when both 5' Gene Expression and V(D)J libraries were sequenced from the same sample.
As shown in the image below, final V(D)J cell calls (intersection area) exclude cells that were only called by the vdj pipeline (yellow region).
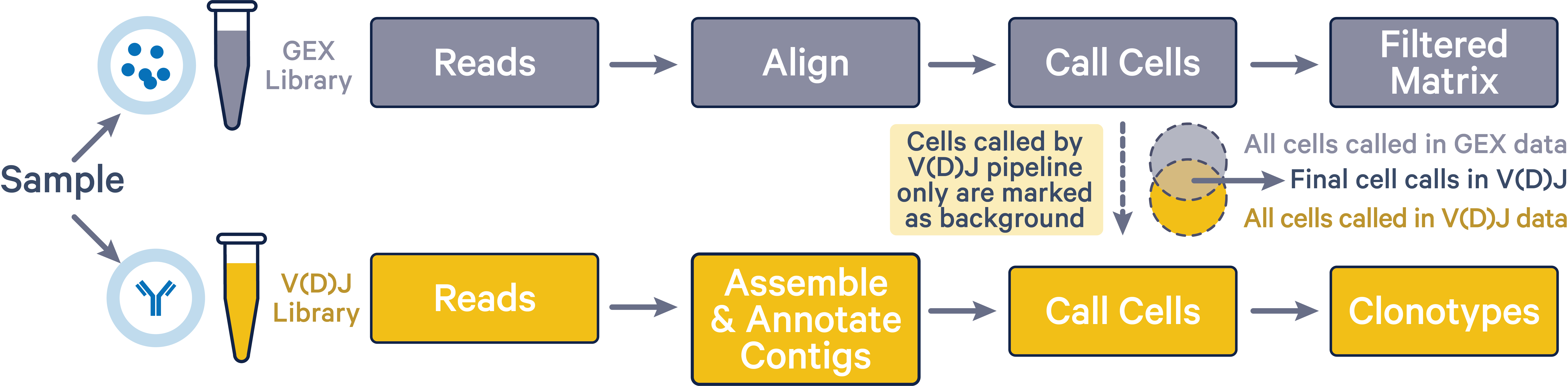
The 5' Gene Expression cell calls are not affected by the cellranger multi pipeline. The Gene Expression library is representative of the entire pool of poly-adenylated mRNA transcripts captured within each GEM. VDJ-T or VDJ-B transcripts in the Gene Expression library are then selectively amplified to create the V(D)J library. Therefore, the Gene Expression library has more power to detect GEMs containing cells compared to the V(D)J library. If the cellranger multi pipeline is run with both 5' Gene Expression and V(D)J data, barcodes that are not called cells in the 5' Gene Expression data are deleted from the V(D)J cell set.
The cellranger multi pipeline takes a config CSV file as input. The config CSV contains paths to FASTQ files for any combination of V(D)J, Gene Expression, and/or Feature Barcode libraries. To generate FASTQ files, follow the instructions for running cellranger mkfastq.
To simultaneously generate single cell feature counts, V(D)J sequences, and annotations for a single library, run cellranger multi with the following arguments:
| Argument | Description |
|---|---|
--id | A unique run ID string: e.g. sample345 that is also the output folder name. Cannot be more than 64 characters. |
--csv | Path to multi config CSV file enumerating input libraries and analysis parameters. |
The multi config CSV contains both the library definitions and experiment configuration variables. It is composed of up to four sections: [gene-expression], [feature], [vdj], [antigen-specificity] and [libraries].
The [gene-expression], [feature], [vdj], and [antigen-specificity] sections have at most two columns and are responsible for configuring their respective portions of the experiment. The [libraries] section specifies where input FASTQ files may be found.
A customizable template for a multi config CSV can be downloaded here, and example multi config CSVs can be downloaded from public datasets. Cell Ranger v7.1 and later also provides the option to download a multi config CSV template via the command line.
Example formats for a few product configurations are below.
Starting in Cell Ranger 7.0, the expected number of cells can either be auto-estimated or specified with expect-cells (e.g., to replicate a previous analysis), see Gene Expression algorithm overview. If needed, automated cell calling can be overridden with the force-cells option.
|
| Multi Config CSV | |
|---|---|
Section: [gene-expression] | |
| Field | Description |
reference | Path of folder containing 10x Genomics-compatible reference. Required for Gene Expression and Feature Barcode libraries. |
target-panel | Optional. Path to a target panel CSV file or name of a 10x Genomics fixed gene panel (pathway, pan-cancer, immunology, neuroscience). |
no-target-umi-filter | Optional. Disable targeted UMI filtering stage. Default: false. |
r1-length | Optional. Limit the length of the input Read 1 sequence of Gene Expression libraries to the first N bases, where N is a user-supplied value. Note that the length includes the Barcode and UMI sequences so do not set this below 26. This and r2-length are useful options for determining the optimal read length for sequencing. Default: do not trim Read 1. |
r2-length | Optional. Limit the length of the input Read 2 sequence of Gene Expression libraries to the first N bases, where N is a user-supplied value. Trimming occurs before sequencing metrics are computed and therefore, limiting the length of Read 2 may affect Q30 scores. Default: do not trim Read 2. |
chemistry | Optional. Assay configuration. NOTE: by default, the assay configuration is detected automatically, which is the recommended mode. Users usually will not need to specify a chemistry. Options are: auto for auto-detection, fiveprime for Single Cell 5', SC5P-PE for paired-end or SC5P-R2 for R2-only, SC-FB for Single Cell Antibody-only. Default: auto. |
expect-cells | Optional. Override the pipeline’s auto-estimate. See cell calling algorithm overview for details on how this parameter is used. If used, enter the expected number of recovered cells. |
force-cells | Optional. Force pipeline to use this number of cells, bypassing cell-calling algorithm. |
include-introns | Optional. Set to false to exclude intronic reads in count. Including introns in analysis is recommended to maximize sensitivity, except when target-panel is used. Default: true |
no-secondary | Optional. Disable secondary analysis, e.g. clustering. Default: false. |
no-bam | Optional. Set this flag to true to skip BAM file generation. This will reduce the total computation time for the pipestance and the size of the output directory. If unsure, we recommend not using this option, as BAM files can be useful for troubleshooting and downstream analysis. Default: false |
check-library-compatibility
| Optional. Allows users to disable the check that evaluates 10x Barcode overlap between libraries when multiple libraries are specified (e.g., Gene Expression + Antibody Capture). Setting this option to false will disable the check across all library combinations. We recommend running this check (default), however, if the pipeline errors out, users can bypass the check to generate outputs for troubleshooting. Default: true |
Section: [feature] | |
| Field | Description |
reference | Optional. Path to Feature reference CSV file, declaring Feature Barcode constructs and associated barcodes. Required only if Feature Barcode libraries are present. |
r1-length | Optional. Limit the length of the input Read 1 sequence of Feature Barcode libraries to the first N bases, where N is a user-supplied value. Note that the length includes the Barcode and UMI sequences so do not set this below 26. This and r2-length are useful options for determining the optimal read length for sequencing. Default: do not trim Read 1. |
r2-length | Optional. Limit the length of the input Read 2 sequence of Feature Barcode libraries to the first N bases, where N is a user-supplied value. Trimming occurs before sequencing metrics are computed and therefore, limiting the length of Read 2 may affect Q30 scores. Default: do not trim Read 2. |
Section: [vdj] | |
| Field | Description |
reference | Path of folder containing 10x Genomics-compatible V(D)J reference. Required for V(D)J Immune Profiling libraries. |
inner-enrichment-primers | Optional. If inner enrichment primers other than those provided in the 10x Genomics kits are used, they need to be specified here as a text file with one primer per line. |
r1-length | Optional. Limit the length of the input Read 1 sequence of V(D)J libraries to the first N bases, where N is a user-supplied value. Note that the length includes the Barcode and UMI sequences so do not set this below 26. This and r2-length are useful options for determining the optimal read length for sequencing. Default: do not trim Read 1. |
r2-length | Optional. Limit the length of the input Read 2 sequence of V(D)J libraries to the first N bases, where N is a user-supplied value. Trimming occurs before sequencing metrics are computed and therefore, limiting the length of Read 2 may affect Q30 scores. Default: do not trim Read 2. |
Section: [libraries] | |
| Column | Description |
fastq_id | Required. The Illumina sample name to analyze. This will be as specified in the sample sheet supplied to mkfastq or bcl2fastq. |
fastqs | Required. The folder containing the FASTQ files to be analyzed. Generally, this will be the fastq_path folder generated by cellranger mkfastq. |
lanes | Optional. The lanes associated with this sample, separated by |. Defaults to using all lanes. |
feature_types | Required. The underlying feature type of the library, which must be one of Gene Expression, VDJ, VDJ-T, VDJ-T-GD, VDJ-B, Antibody Capture, Antigen Capture (for BEAM library), or CRISPR Guide Capture. To analyze an antigen library created using an antigen-multimer staining assay (TotalSeq™-C, Immudex's dMHC Dextramer® libraries with dCODE Dextramers), set feature_types to Antibody Capture. Setting to VDJ will auto-detect the chain type. |
subsample_rate | Optional. The rate at which reads from the provided FASTQ files are sampled. Must be a number between 0 (no reads sampled) and 1 (all reads included). |
For help on how to configure the [libraries] section to target a particular set of FASTQs, consult Specifying Input FASTQ Files for cellranger multi.
|
After determining the input arguments, run cellranger multi. Remember to replace the bits of code in red with your sample id and csv file path:
mkdir /home/jdoe/runs cd /home/jdoe/runs cellranger multi --id=sample345 --csv=/home/jdoe/sample345.csv
Following a series of checks to validate input arguments, cellranger multi pipeline stages will begin to run:
Martian Runtime - v4.0.8 Running preflight checks (please wait)... ...
By default, cellranger will use all of the cores available on your
system to execute pipeline stages. You can specify a different number of cores
to use with the --localcores option; for example, --localcores=16
will limit cellranger to using up to sixteen cores at once. Similarly,
--localmem will restrict the amount of memory (in GB) used by
cellranger.
The pipeline will create a new folder named with the run ID you specified using the --id argument (e.g. /home/jdoe/runs/sample345) for its output. If this folder already exists, cellranger will assume it is an existing pipestance and attempt to resume running it. If you wish to re-start the run, delete the output folder (sample345/ in this example) and rerun the pipeline.
A successful cellranger multi run should conclude with a message similar to this:
Waiting 6 seconds for UI to do final refresh. Pipestance completed successfully! yyyy-mm-dd hh:mm:ss Shutting down. Saving pipestance info to "tiny/tiny.mri.tgz"
To learn more about the output files generated, refer to the Outputs for multi section under Understanding Outputs.
Cell Ranger multi v7.0.0 and later allows users to analyze T cell libraries enriched for gamma (TRG) and delta (TRD) chains. 10x Genomics does not provide reagents or primers for TRG/D chain enrichment. Since this workflow is not fully supported, the Cell Ranger pipeline has not been extensively tested for TRG/D libraries, and the algorithm's performance cannot be guaranteed.
To analyze TRG/D libraries, set feature_types to VDJ-T-GD in the [libraries] section of the multi config CSV. Auto-detection does not work for TRG/D chains. If set to auto-detection, TRG/D libraries are treated as VDJ-T libraries enriched for alpha-beta chains, and the gamma-delta chains are filtered out. The pipeline runs to completion, but zero barcodes are assigned to cells.
Refer to the example multi config CSV for additional configuration guidance. Outputs from a successful gamma-delta run are located in the vdj_t_gd folder.
The cellranger vdj pipeline cannot process FASTQs from TRG/D enriched libraries.
In the [libraries] section of the multi config CSV, setting feature_types to VDJ enables auto-detection of the chain type.
feature_types set to VDJ fails when both VDJ-T and VDJ-B FASTQ sets are included.VDJ, VDJ-T, VDJ-B, or VDJ-T-GD, and the combinations:
VDJ-T & VDJ-BVDJ-T-GD & VDJ-BVDJ-T & VDJ-T-GD & VDJ-BVDJ), gamma-delta libraries are treated as VDJ-T and gamma-delta chains are filtered out. The pipeline runs to completion, but zero barcodes are assigned to cells. For TRG/D chains, set feature_types to VDJ-T-GD.Auto-detection is enabled for Antigen Capture (BEAM) libraries. Use feature_types = Antigen Capture for both TCR and BCR Antigen Capture libraries.
Cell Ranger v7.1 enables users to download a multi config CSV template by running:
cellranger multi-template --output=/path/to/FILE.csv
Remember to replace code in red with the path to directory in which you wish to output the template. Omitting the file path downloads the file into your working directory. After downloading, please remember to customize the template based on your assay and experimental design.
To print a list and description of all configurable parameters available in cellranger multi, run
cellranger multi-template --parameters
Specifying both --parameters and --output will output a parameter documentation file. Run cellranger multi-template --help or cellranger multi-template -h for more information about available flags.
Here are the example multi config CSVs for a few commonly used library combinations. Make sure to replace /path/to with the actual full path to your data, and edit any text in red according to the experiment's sample/library/file names. TRG/D and Antigen Capture config examples are located on their respective pages.
| Libraries | Multi config CSV | ||||||
 See example dataset |
[vdj] reference,/path/to/vdj_reference [libraries] fastq_id,fastqs,feature_types VDJ_B_fastqs_id,/path/to/vdj_B_fastqs,VDJ-B |
The cellranger multi pipeline supports downsampling the reads by specifying a rate between 0 and 1 independently for each library. It also allows trimming the reads to a fixed length, which is not supported in the cellranger vdj pipeline.
The option to run denovo without V(D)J reference (--denovo) is not supported in cellranger multi. This option is available in cellranger vdj.
Next, you may wish to: