Cell Ranger ATAC3.0, printed on 04/05/2025
You can save your dataset workspace, including any custom clusters and feature lists you've created by clicking on the Save (disk) icon on the toolbar.
If you prefer to create a new version of a .cloupe file, choose Save As from the File menu, or press Ctrl-Shift-S (Windows) or Command-Shift-S (Mac). You are prompted to create a new .cloupe file somewhere in your file system.
Loupe Cell Browser files are self contained, so if you want to share a dataset with a colleague, you can send him or her the .cloupe file.
There are many scripts and packages in the single-cell analysis ecosystem so you may want to import and export cluster labels into and out of Loupe Cell Browser. Select Categories mode, click on the action button to the right of the active category name, and select one of the import/export options.
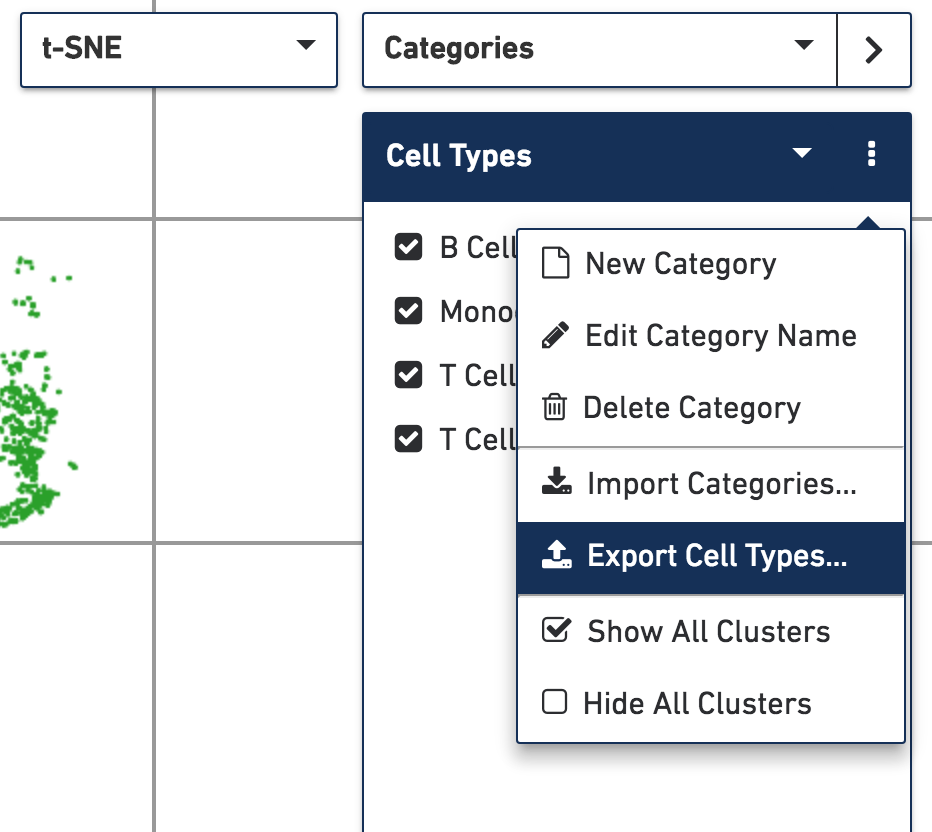
Cluster labels are stored in CSV format. When importing cluster label CSVs into Loupe Cell Browser,
barcodes must be in the first column, the first row must be a column header, the barcode column header must be named barcode, and the values of the barcodes must match at least a subset of the
barcodes in the .cloupe file. To get a sense of the CSV structure, you can Export one of the
pre-defined categories in your dataset, and view it with a text editor or spreadsheet tool.
There are a variety of mechanisms to export data and graphics from your ATAC dataset. The toolbar, categories list, feature list, feature table. and peak viewer all have export functionality.
Export functions include:
Exporting Barcode Plots - Clicking on the camera icon in the toolbar exports the currently-displayed barcode plot. You can choose to export to either PNG, or SVG vector formats. The SVG vector format includes axes if Feature Plot view is active.
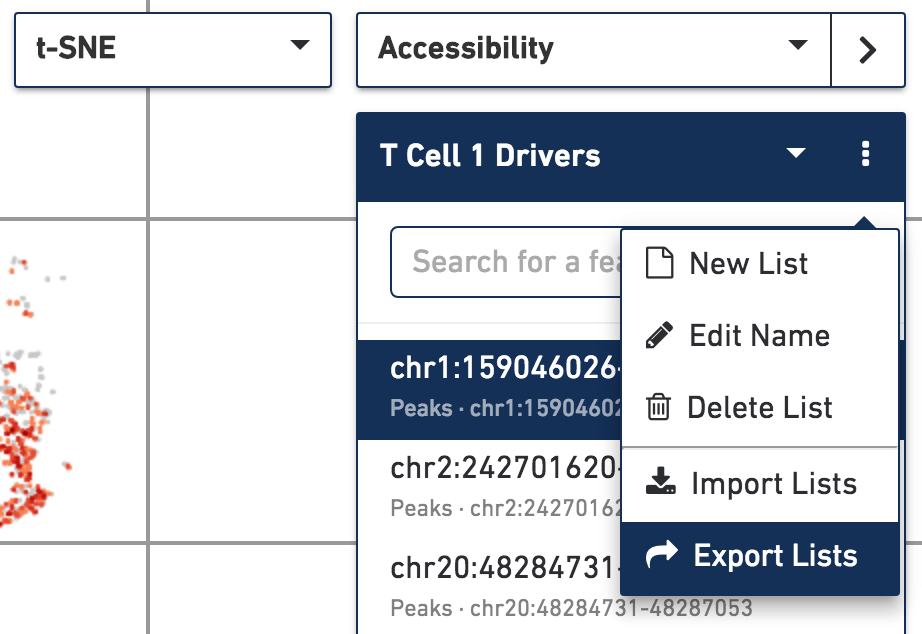
Exporting Feature Lists - With Accessibility mode selected, you can choose to import a set of feature lists, or export the currently loaded set of feature lists. Click on the action button to the right of the feature list selector to do so. Motifs and promoter sums should be applicable across multiple datasets, though lists with peaks will likely not translate between datasets.
Exporting Significant Features - To export the tabular list of significant features, including p-values and log2 fold changes, click on the Export icon above the feature table. This saves the current table in CSV format. You can use the Feature Options menu to select enriched features, depleted features, the number of features to export in CSV format, and whether to filter by an average accessibility level across the dataset.
Exporting Peak Viewer Plots - Finally, with the Peak Viewer active, you can click the Export button to export the currently visible peaks into a CSV file, visible cut sites into a multi-track .bedgraph file, or the peak viewer plot into PNG or SVG format.
This concludes the Loupe Cell Browser ATAC tutorial. Now it's time to use what you've learned on your own data. Read about how to generate your own .cloupe files with the Cell Ranger ATAC pipeline.
If you encounter any errors in the program, you can send a bug report at any time by clicking on Generate Bug Report from the Help menu. A .tar.gz file containing logs from your most recent Loupe Cell Browser session is created, and you can send that file to support@10xgenomics.com. Add the subject line Loupe Cell Browser Error to your message.
You can also submit general feedback and feature requests to support@10xgenomics.com as well.
We hope this tutorial has made you familiar with the capabilities of Loupe Cell Browser, and made you excited to process your own data. We hope you find it to be the easiest, fastest and most enjoyable way to interpret your single-cell ATAC data.